Post-Quantum Encryption – Protection for a Peaceful Future
Almost every business that manages data and maintains customer relationships through an encrypted channel must be aware of the IT advances and technology changes that quantum computers mean. The encryption procedures currently in place become easily cracked with the advent of high-performance quantum computers. Most experts say it will happen in no more than 10 years, or even much earlier. This affects all asymmetric encryption procedures, including digital signatures and bank gateways. Many other public and private services can also be named here, as well as browsers.
What exactly the Quantum does?
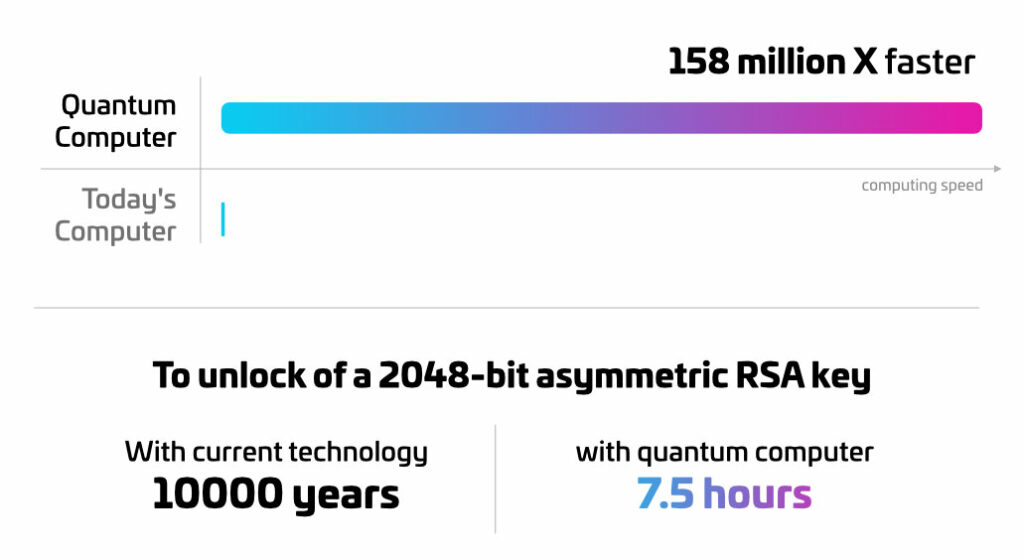
Quantum computers perform calculations much faster than current computers, potentially capable of up to 158 million times more performance. This means that what currently would take 10,000 years would be solved by a quantum computer in 7,5 hours. This is based on qubits, which are replacing binary-based bits. Qubits not only occur in a specific position (0,1), but in both at the same time, assuming a superposition.
The current largest reported quantum computer is 127 qubits. This is not a significant performance. It is almost certain that a quantum computer capable of much higher performance already exists. The creator of such a computer does not reveal every detail of its development. The reason for this is that the first to build a high-performance quantum machine will have a huge advantage in many areas. It is enough to think about what it means in the field of astronomical measurements and research. Tasks which today take 10 million years to the best of our current knowledge will be carried out within a reasonable time. Potential options include breaking a significant portion of the encryption procedures currently considered secure.
In theory, encryption codes can be cracked also now. In practice it requires complex, lengthy computations that have so far been unsolvable with available technology. With the multiplier speed of quantum computers, this hurdle is overcome. That was proved by American mathematician Peter Shor, who received numerous awards for the Shor algorithm named after himself, alsot the Gödel Prize in 1999, one of the most significant mathematical awards.
Preparation
Governments have also begun preparations for the quantum era. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), announced the development of standards for post-quantum encryption procedures as early as 2016. The competition calls tech companies to create procedures that provide protection against quantum computers in the post-quantum era.
Preparations have started not only overseas, but also in Hungary. In 2021 an amendment of the law named the state and market actors (e.g. banking sector) that must have post-quantum encryption. It designated the organization which later will clarify the scope of companies required to post-quantum encryption. This organization is responsible also for registering companies offering such procedures and for issuing certificates to them.
False sense of security or excessive sense of danger?
The answer is a bit “dependent” on what we will defend.
In the case of cryptographic protections related to integrity and authenticity, we are able to “protect” our systems, files and data up to the penultimate moment before the appearance of the quantum computer. In any case, it is recommended to prepare and make the transition much earlier, because it is not a 1-2-months project.
However, we’re long overdue on encryption: anyone who saves encrypted data today will be able to decrypt it with a quantum computer and will have the possibility to create a new WikiLeaks portal in the quantum era. So, change is definitely a current need here, and it can already be found in some sectors.
This is not just an imagined scenario from the future. Behind the boycott of Huawei, one of the main battles of the U.S.-China trade war, there were also considerations that the Chinese telecommunication company would process the browsing history of users and their environment with quantum computers.
Our research and development
The experts of the E-Group Data & Trust Lab started research on the topic in 2015 and developed a post-quantum e-signature solution. So, we can say that E-Group is forming one of the most prepared teams in Hungary. Recently, experts from E-Group, BME, Magyar Telekom, Nokia Bell Labs and Ericsson Hungary discussed the topic at the HTE Infokom conference. Finding the right algorithm is essential in both the government and corporate sectors. At present they study the 7 potential algorithms as technological experts. They make comparative analyzes to create the most competitive solution in Hungary that meets the American standard.
The race has started and it would be a mistake to think that you don’t have to participate and just have to cheer from the stands.
If you have any questions or need advice, contact E-Group’s team of experts!


